
Master reverse logistics to turn returns into profits. Boost efficiency, customer loyalty, and sustainability in your online retail business.
Handling returns isn’t the most glamorous part of running an online store, but it’s one of the most important. Every product that flows back into your business has the potential to erode profit margins, frustrate customers, and create operational headaches—or to become an opportunity for efficiency, loyalty, and even new revenue. That’s where reverse logistics comes in.
Reverse logistics is more than just “dealing with returns.” It’s the full process of receiving, inspecting, repairing, reselling, recycling, or disposing of products that come back through your supply chain. When done poorly, it can drain time, money, and goodwill. When done well, it becomes a competitive advantage—turning what many retailers see as a cost center into a value recovery engine.
In ecommerce, where return rates are significantly higher than in brick-and-mortar retail, having a clear and effective reverse logistics process isn’t optional. It’s essential for customer satisfaction, operational efficiency, and long-term profitability.
Understanding Reverse Logistics in Ecommerce
Reverse logistics flips the conventional product flow on its head. Instead of moving goods from manufacturers to consumers, reverse logistics handles products traveling backward through the supply chain—from customers back to retailers or manufacturers.
What makes reverse logistics different from forward logistics?
The direction of product flow represents the most obvious difference between reverse and forward logistics. Forward logistics pushes products toward customers, while reverse logistics pulls products back from consumers to sellers. This reversal creates several unique characteristics that make the process fundamentally different.
Reverse logistics isn’t typically planned by businesses but happens in response to customer actions. This reactive nature makes volume prediction challenging, since returns occur on customers’ schedules rather than company timelines. You can’t exactly tell your customers when to return their purchases.
The processes involved differ significantly as well. Forward logistics focuses on distribution and delivery, but reverse logistics encompasses a much broader range of activities:
- Returns processing and authorization
- Inspection and sorting of returned items
- Refurbishment and repair
- Recycling and responsible disposal
- Repackaging for resale or restocking
Each returned item needs individual assessment to determine whether it can be resold at full price, discounted, refurbished, recycled, or disposed of. This individualized handling makes reverse logistics more labor-intensive and costly per unit than forward logistics, where products move in predictable batches.
The goals differ too. Forward logistics aims to get products to customers efficiently, whereas reverse logistics strives to recapture value from items coming back through the supply chain. It’s about damage control and value recovery rather than pure distribution.
Why online retailers need a reverse logistics strategy
Online retailers face a particularly brutal returns challenge. Approximately 30% of online purchases get returned, compared to only about 10% of in-store purchases. This dramatically higher return rate makes effective reverse logistics crucial for ecommerce businesses.
A well-designed reverse logistics strategy offers several key advantages beyond just managing high volumes:
- Customer loyalty and satisfaction. Over 60% of online shoppers review a retailer’s return policy before making a purchase. A transparent, hassle-free return policy builds trust and encourages initial purchases. A positive return experience also increases the likelihood of repeat business—something you can’t afford to ignore.
- Cost reduction opportunities. Returns represent a significant expense, but optimized reverse logistics processes can minimize these costs through efficient inventory management, streamlined operations, and reduced waste. Without an effective system, the labor-intensive processes of inspecting, repackaging, and restocking returned items become unnecessarily expensive.
- Value recovery. Rather than treating returns as pure losses, effective reverse logistics allows businesses to recapture value through refurbishment, repackaging, or recycling. This creates potential for new revenue streams from items that would otherwise represent complete losses.
- Sustainability benefits. Proper reverse logistics supports environmental goals by extending product lifecycles through refurbishment and upcycling. For environmentally conscious consumers, these practices also enhance brand perception.
- Competitive advantage. Consumer expectations for seamless returns continue to grow. Companies with superior reverse logistics capabilities gain an edge over competitors who treat returns as an afterthought.
Creating an effective reverse logistics strategy isn’t optional for online retailers—it’s a business necessity that affects customer satisfaction, operational efficiency, and your bottom line.
Key Components of the Reverse Logistics Process
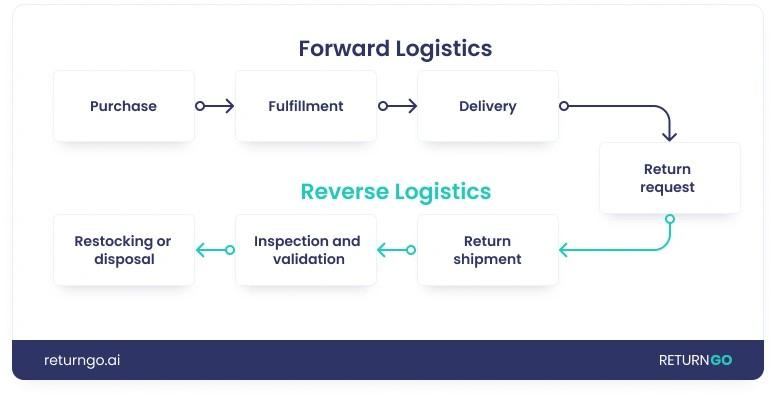
Image Source: ReturnGO
Effective reverse logistics starts with a structured process. When products flow backward through your supply chain, clear procedures determine whether you recover maximum value from returns or watch money disappear.
Returns initiation and authorization
The reverse logistics journey begins the moment a customer decides to return a product. Most online retailers handle this through return requests submitted via their website or app. What happens next makes the difference between smooth operations and customer frustration.
Most ecommerce businesses rely on a Return Merchandise Authorization (RMA) system that validates returns against your policy and provides shipping instructions. An effective RMA process handles four critical tasks:
- Captures essential return details and reasons
- Verifies purchase information and return eligibility
- Provides clear return shipping instructions
- Generates pre-paid shipping labels for convenience
The returns initiation process is vital because it sets customer expectations and creates your first data point for tracking returns patterns.
Inspection and sorting of returned items
Once returned items reach your warehouse or processing center, each product needs individual inspection. This sorting phase determines how much value you’ll recover from returns.
Your team categorizes returns into disposition groups during inspection. The standard categories include:
- Resellable as new (unopened, undamaged)
- Resellable as returned (opened but functional)
- Requires repair or refurbishment
- Suitable for recycling
- Unsalvageable (disposal required)
Speed matters here. The inspection process should happen immediately to prevent delays that cause returnable inventory to lose value. Many retailers use barcode scanning during inspection to update inventory records and maintain tracking accuracy.
Repair, refurbish, or recycle decisions
After inspection, you face a critical decision point for each returned item. This choice directly impacts both profitability and sustainability of your reverse logistics operation.
Items needing repair should move quickly to your returns department for examination. Your team determines what repairs are possible and either completes the work or salvages usable parts for future construction.
Refurbishment involves cleaning, component replacement, or other restoration before the item re-enters inventory—usually as discounted or “refurbished” merchandise.
Products beyond repair require proper recycling procedures. Items that can’t be fixed, salvaged, reused, or resold go to designated recycling areas. This step grows more important as sustainability becomes a consumer priority.
Restocking or resale of returned goods
The final phase reintroduces sellable items into your inventory system. Returns passing inspection as “like new” rejoin primary inventory for full-price sales.
Opened or slightly used items that remain functional work better through alternative channels:
- Discounted website sections
- Secondary marketplaces for open-box items
- Outlet stores or liquidation partners
Update your inventory systems immediately to reflect accurate stock levels. This prevents double-selling items or inventory errors that affect purchasing decisions.
Some retailers create dedicated channels specifically for refurbished merchandise to avoid mixing with new inventory. This approach creates separation between new and renewed products, protecting your primary sales channels from potential negative impacts.
What Actually Happens in Reverse Logistics
Reverse logistics isn’t just “handling returns.” It’s a collection of distinct activities that online retailers need to master. Understanding these components helps you build more efficient processes and squeeze maximum value from every returned item.
Returns and exchanges
Let’s face it: nearly 75% of retailers consider returns a necessary evil. U.S. retailers dealt with about $428 billion in returned merchandise in 2020—that’s 10.6% of total retail sales. Ecommerce gets hit even harder, with roughly 18% of online purchases coming back.
Customer returns happen for all sorts of reasons—poor fit, unmet expectations, or simple buyer’s remorse. Your return policy carries serious weight here. A staggering 84% of consumers say the returns experience shapes their opinion of a retailer. Even more telling: 60% of online shoppers actually read return policies before buying.
Smart approaches include:
- Simple return forms that capture why customers are sending items back
- Including return shipping labels right in the original packaging
- Standardizing your inbound processing procedures
Refurbishment and recommerce
Refurbishment extends product life and cuts down on new manufacturing needs. The process focuses on fixing actual problems rather than preventing future ones. While less intensive than full remanufacturing, refurbished items tap into a solid market segment.
Here’s where it gets interesting: recommerce (reselling previously owned items) offers massive opportunity. About 80% of returned merchandise can actually be resold. This circular system—return, refurbish, resell—creates a powerful way to recover revenue that would otherwise vanish.
Recycling and disposal
Some products can’t be resold or refurbished. That’s when proper recycling and disposal become essential. This applies to items too damaged for your inventory or when customers send in old products for responsible disposal.
Waste reduction sits at the heart of reverse logistics. You need to identify and minimize waste throughout your processes while ensuring hazardous or non-recyclable materials get disposed of properly.
Packaging reuse and delivery failures
Reusable packaging often beats single-use options across environmental metrics. The benefits stack up: less material consumption, lower carbon emissions, reduced water use, and better palletization efficiency.
Delivery failures create another reverse logistics headache. When shipments fail due to unexpected circumstances, products flow back to fulfillment or sorting centers. Staff then diagnose the issue and either send items back to manufacturers or fix problems at the sorting center before putting products back into circulation.
Managing these activities properly transforms returns from a pure expense into a potential revenue stream while supporting your sustainability goals.
Best Practices for Reverse Logistics Management
Smart returns management transforms a costly process into a strategic advantage. The right approach helps recover value from returned items while building the customer trust that drives repeat business.
Create a clear return policy
Your return policy drives purchase decisions. Studies show 67% of shoppers check the return page before buying. A solid policy should be easy to find and understand, clearly answering three questions customers actually care about:
- Can the item be returned?
- How much time is available for returns?
- Will the return cost anything?
Make your policy visible in your website footer, on product pages, and in shopping carts. Straightforward language builds customer confidence and cuts down on support team questions. When crafting your policy, consider offering exchanges or store credit instead of just refunds. This approach keeps revenue within your business rather than losing it completely.
Collaborate with logistics partners
The right logistics partnerships create smooth, integrated customer experiences. Many third-party logistics providers (3PLs) now specialize in returns handling, using robotics and AI to process high volumes efficiently. Companies like Green Wave Electronics 3PL can be valuable for retailers managing electronics returns, where refurbishment, recycling, and redistribution require specialized expertise.
The Reverse Logistics Association reports over 5,000 companies involved in reverse logistics, making partnerships increasingly valuable. The right logistics partner extends your capabilities without overwhelming your in-house team, especially for specialized returns like hazardous materials or electronics.
Use centralized return centers
A dedicated returns facility streamlines your entire reverse logistics operation. With a centralized return center, you can better sort products and determine the most appropriate next step for each item. This focused approach lets your team concentrate exclusively on evaluating returns instead of juggling multiple warehouse operations.
If establishing a separate returns center isn’t realistic, dedicate a specific warehouse area solely for returns processing. Either way improves efficiency by creating standardized procedures for handling incoming items.
Automate tracking and processing
Automation speeds up returns processing while slashing human errors. Cloud-based logistics software streamlines operations by tracking asset recovery, managing refurbishments, and providing business intelligence.
An automated system instantly verifies if items qualify for return based on your policies, ensuring consistency and reducing costly mistakes. Real-time tracking gives customers visibility into their return status and helps your team spot delays or issues immediately.
The bottom line is that these practices create a more efficient returns process that satisfies customers and minimizes costs throughout your reverse logistics operations.
Optimize Reverse Logistics for Maximum Impact
Optimizing your reverse logistics operations saves money and turns returns into opportunities. National Retail Federation data shows over $743 billion in merchandise was returned in 2023, making efficient returns management essential for profitability.
Use data to slash return rates
Returns data reveals patterns that most retailers ignore. Why do customers return products? The answer helps you make smarter decisions about everything from product descriptions to personalized recommendations.
Strategic return data collection helps predict trends, address systemic issues, and personalize the consumer experience. Returns analysis pinpoints specific problems like:
- Sizing inaccuracies
- Design flaws
- Damage during transit
- Delivery route delays
Companies using data analytics have cut return rates by up to 20%. That’s a direct hit to your bottom line.
Connect returns with your inventory systems
Your returns process needs to talk to your inventory management. Cloud-based logistics software streamlines operations by tracking asset recovery, managing refurbishment, and providing business intelligence analytics.
Mathematical models of inventory management in reverse logistics systems help optimize holding costs. With centralized tracking, businesses can better sort products and identify the best next steps for each item.
Real-time visibility across your supply chain changes everything.
Give customers return flexibility
Modern consumers expect options when returning products. Omnichannel returns let customers return items through any channel they prefer—regardless of where they purchased. Smart options include:
- In-store returns for online purchases
- Return through mobile apps or websites
- Choice between refunds, exchanges, or store credit
This approach improves customer satisfaction, with research showing consumers are more loyal to brands offering streamlined returns processes.
Invest in durable, reusable packaging
Sustainable packaging solutions support both environmental goals and return efficiency. Reusable packaging handles multiple shipments without breaking down, reducing the need for new materials with each return.
For frequently returned items like clothing and footwear, reusable packaging makes perfect sense. Benefits include fewer purchases of disposable boxes, lower disposal bills, and improved handling efficiency in reverse logistics.
Well-designed reusable packaging folds when empty to optimize space yet stays sturdy enough to endure multiple transportation cycles. It’s ideal for efficient returns processing.
The Bottom Line
Reverse logistics isn’t a side project—it’s a profit lever, a brand differentiator, and a customer loyalty engine rolled into one. The retailers who master it don’t just reduce losses; they actively reclaim value and deepen trust with their audience. By approaching returns as a strategic process—rather than a necessary evil—you position your business to respond faster, recover more revenue, and deliver a better overall experience.
The tactics in this guide give you a framework to streamline operations, cut waste, and meet customer expectations without sacrificing profitability. But the real impact comes from execution. Small refinements—like tightening inspection workflows, integrating return data into inventory systems, or offering flexible return options—compound over time into major efficiency gains.
Sustainability also plays a growing role in reverse logistics. From reusable packaging to responsible recycling, the way you handle returned products speaks volumes about your values and your commitment to long-term brand reputation.
Ultimately, reverse logistics is about more than moving goods backwards—it’s about moving your business forward. Those who invest in it now will outpace competitors, retain more customers, and turn every return into an opportunity.
Was this news helpful?







 Yes, great stuff!
Yes, great stuff! I’m not sure
I’m not sure No, doesn’t relate
No, doesn’t relate



